absorption cooling units

The concept of solar cooling is appealing because the cooling load is in phase with the intensity of solar energy. Many system arrangements or cycles are employed to achieve solar cooling, such as Absorption, desiccant or Rankine-vapour compression systems. The technical feasibility of driving an absorption-cooling unit by a low-temperature heat source (such as solar energy using a simple flat-plate collector) for air-conditioning applications is investigated in this work.This study aims to design and construct a prototype for an intermittent absorption refrigeration system and to examine its implementation. The operating characteristics of the considered unit are extensively investigated. In order to accomplish this strategy, the prototype was integrated in a test rig designed for this purpose and equipped with the necessary measuring instruments to determine the required operating criteria of the unit. The energy added or extracted to or from the different unit components is calculated and the system performance is analysed.

The C.O.P of the unit is found to be 19% which is 2% lower than the designed value, which could be regarded as an encouraging result for more studies in this field. Copyright © 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.Yazaki Water-Fired SINGLE-EFFECT chillers have cooling capacities of 5, 10, 20, 30, and 50 tons of refrigeration. Chiller-heaters have cooling capacities of 10, 20, and 30 tons of
amps for ac unitBoth produce chilled water for cooling and chiller-heaters also provide hot
ac unit soft start water for heating in comfort air conditioning applications.
automobile ac unitsThe absorption cycle is energized by a heat medium (hot water) at 158°F to 203°F from an industrial process, cogeneration system, solar energy or other heat source and the condenser is water cooled through a

Compare Steam operated LiBr absorption chillers New Vision (Beijing) Technology And Trade Co., Ltd. US $220-290 1 Unit Transaction Level Heat Pumps Come in Many Styles Fall 2015 Technical Training Class Robur Corporation would like to invite you to attend the Fall Technical Training class on Robur’s latest absorption cooling and heating technology scheduled for October 20th, 21st and 22nd, 2015. Will a brown out or power outage affect the operation of the unit? Plate Type Heat Exchanger Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger Gasket Plate Heat Exchanger Apv Plate Heat Exchanger Gea Plate Heat Exchanger Wind Turbine Oil Cooler Commercial Refrigerator & Freezer Optical Lens & Instrument Single-Effect Low-Temperature Hot Water Absorption Chiller 75 to 525 Nominal Tons Single-effect absorption chillers are commonly installed in large capacity comfort cooling applications that are also served by centrifugal or screw chillers such as office buildings, hospitals and universities as well as manufacturing facilities and light industrial process cooling.
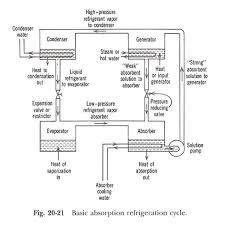
They are also often used in hybrid plant applications, which involve both electric and absorption chillers, and are an ideal choice where waste heat is available or where electric rates and/or demand charges are high. HVAC System Design Software Written by HVAC System Designers Receive Ongoing Expert HVAC System Info Absorption chillers are energized by flue gas or hot water to provide chilled water for air conditioning systems or industrial cooling applications. Packages designed to reduce engineering, installation, and maintenance costs Interior or exterior applications Supplied as a chiller or a chiller heater Fluids – Lithium bromide, water, or ammonia vapor Single hermetic pump controls solution flow Built in shutdown controls Ideal for a two pipe hydronic system in which chilled water or hot water is circulated to a central air handling unit or multiple fan coil units The absorption chiller or chiller-heater uses a solution of lithium-bromide, water, or ammonia vapor, under a vacuum, as the working fluid.

Water is the refrigerant and lithium bromide, a nontoxic salt, is the absorbent. Refrigerant, liberated by heat from the solution, produces a refrigerating effect in the evaporator when cooling water is circulated through the condenser and absorber. C65 kW produces 20-30 Tons of Chilled Water C200kW produces 60 Tons of Chilled Water C600kW produces 180 Tons of Chilled Water C800kW Produces 240 Tons of Chilled Water C1000kW Produces 300 Tons of Chilled water Design and Analysis of a Solar Assisted Absorption Cooling System Integrated with Latent Heat Storage Infante Ferreira, C.A. (mentor) Mechanical, Maritime and Materials Engineering Sustainable Process and Energy Technology Air conditioning is one of the major consumers of electrical energy in many parts of the world. The demand can be expected to increase because of the changing working times, increased comfort expectations and global warming. With more air conditioning units, the electricity demand has been rising thereby increasing the use of fossil fuels and nuclear energy.

A drastic change, therefore, should be implemented in the energy structure of the developed countries. Environmentally friendly and energy efficient technologies should be introduced in which the environmental impact of the conventional air conditioning system is minimized. Solar radiation as a sustainable energy resource is one of the most available forms of energy on the earth surface which could reduce the fossil fuel consumption and CO2 emission to the atmosphere. Solar cooling is a possible technological alternative to conventional air conditioning systems that has recently attracted a growing interest. A solar assisted absorption cooling system as a sustainable solution for cooling systems could provide both heating and cooling of a building. Since the solar energy is available for only a fraction of the day and its availability depends on several factors such as latitude and sky clearness, the storage of it is an important concern. Thermal energy storage is a practical way in conserving the solar energy as it can reduce the discrepancy between the energy supply and demand.

Latent heat storage units (LHSU) using Phase Change Materials (PCMs) are promising candidates as heat storage media. In this thesis, the behavior of a solar assisted single effect absorption system integrated with LHSU was investigated. The mathematical model for the single effect absorption system and the LHSU based on the mass and energy balances and heat transfer equations were developed. The models were implemented in MATLAB and the numerical results were validated with the experimental results from the literature. Based on the cooling demand of a specific building (waiting room in Schiphol airport) the absorption system and the LHSU were designed and the behavior of each system for different control parameters is investigated. For the designed single effect absorption system, variation of the COP and the evaporator heat transfer rate at the different flow rates and temperatures of the external cool water, hot water and the chilled water were studied. The results show that the chilled, hot and cooled water temperatures have significant effect on the performance of the absorption system.